8 Model Evaluation
Model evaluation involves assessing the performance of a machine learning model using various metrics and techniques.
8.1 Performance Metrics
8.1.1 Confusion Matrix
A table used to describe the performance of a classification model, showing the counts of true positive, true negative, false positive, and false negative predictions.
load("data/data_imputed.rda", verbose = TRUE)
Loading objects:
data_imputed
load("data/train_test_data.rda", verbose = TRUE)
Loading objects:
train_data
test_data
load("models/models.rda", verbose = TRUE)
Loading objects:
mod_glmnet_adcv
mod_regLogistic_cv
mod_rf_adcv
mod_rf_reptcv
mod_knn_adcv
mod_knn_reptcv
# Load necessary libraries
library(caret)
# Predict using the trained model
predictions <- predict(mod_regLogistic_cv, newdata = test_data)
# Compute confusion matrix
confusion_matrix <- caret::confusionMatrix(predictions, test_data$target)
print(confusion_matrix)
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction 0 1
0 19 3
1 5 16
Accuracy : 0.814
95% CI : (0.666, 0.9161)
No Information Rate : 0.5581
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 0.000393
Kappa : 0.6269
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.723674
Sensitivity : 0.7917
Specificity : 0.8421
Pos Pred Value : 0.8636
Neg Pred Value : 0.7619
Prevalence : 0.5581
Detection Rate : 0.4419
Detection Prevalence : 0.5116
Balanced Accuracy : 0.8169
'Positive' Class : 0
8.1.3 Precision
The proportion of true positive predictions out of all positive predictions. It measures the model’s ability to identify relevant instances.
8.1.4 Recall (Sensitivity)
The proportion of true positive predictions out of all actual positive instances. It measures the model’s ability to capture all positive instances.
8.1.5 F1 Score
The harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a balance between the two metrics. It is useful when the class distribution is imbalanced.
Performance metrics dataframe
# Create a data frame for model performance metrics
performance_metrics <- data.frame(
Metric = c("Accuracy", "Precision", "Recall", "F1 Score"),
Value = c(accuracy, precision, recall, f1)
)
performance_metrics
Metric Value
Accuracy Accuracy 0.8139535
Precision Precision 0.8636364
Recall Recall 0.7916667
F1 F1 Score 0.8260870Visualize model performance metrics
ggplot(performance_metrics, aes(x = Metric, y = Value)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", fill = "steelblue", color = "black") +
labs(x = "Metric", y = "Value", title = "Model Performance Metrics") +
theme_minimal()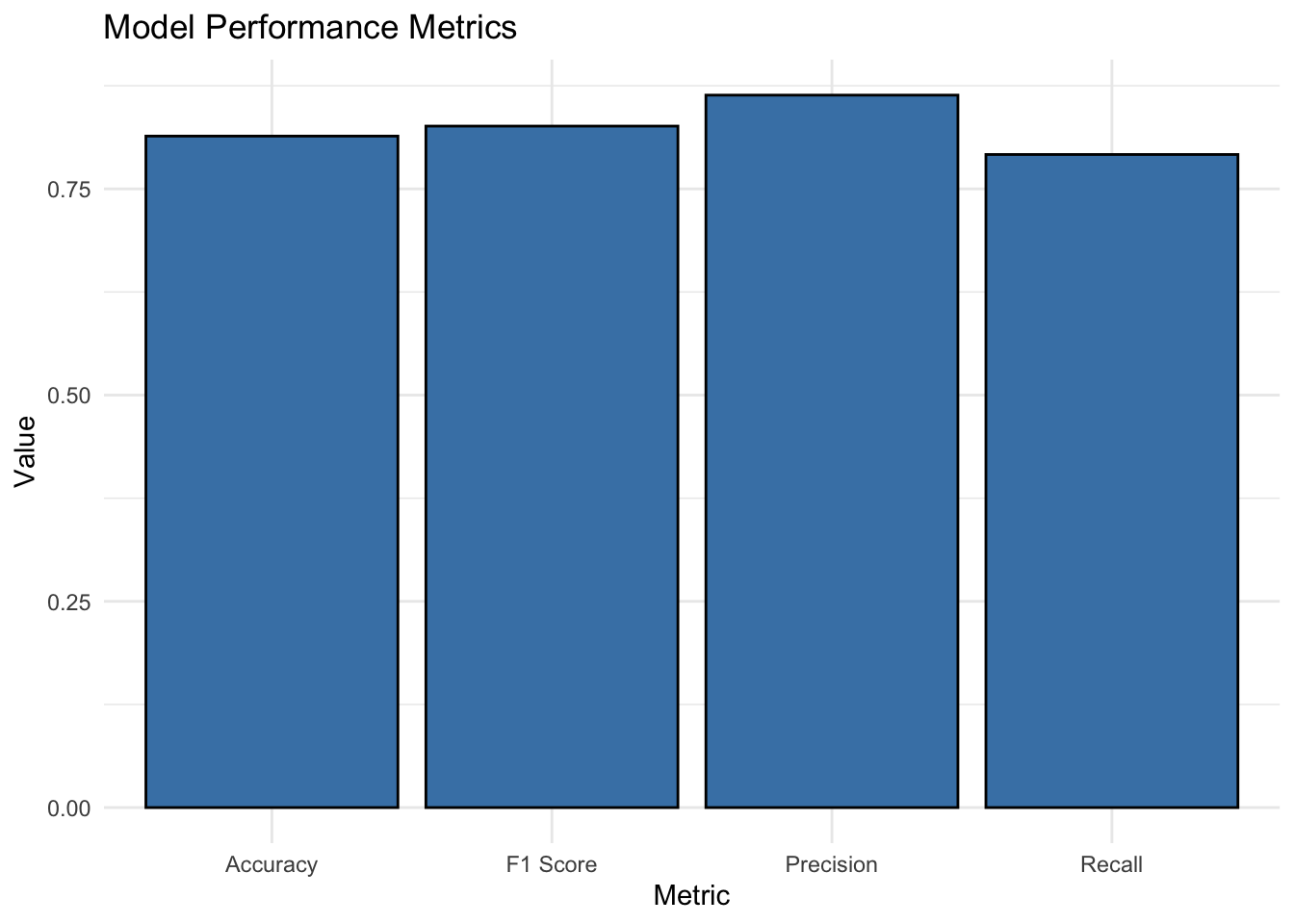
Function for computing Specificity and Sensitivity
library(purrr)
get_sens_spec <- function(threshold, score, actual, direction){
predicted <- if(direction == “greaterthan”) { score > threshold } else { score < threshold }
tp <- sum(predicted & actual) tn <- sum(!predicted & !actual) fp <- sum(predicted & !actual) fn <- sum(!predicted & actual)
specificity <- tn / (tn + fp) sensitivity <- tp / (tp + fn)
tibble(“specificity” = specificity, “sensitivity” = sensitivity) }
get_roc_data <- function(x, direction){
# x <- test # direction <- “greaterthan”
thresholds <- unique(x$score) %>% sort()
map_dfr(.x=thresholds, ~get_sens_spec(.x, x\(score, x\)srn, direction)) %>% rbind(c(specificity = 0, sensitivity = 1)) }
8.2 ROC Curve and AUC-ROC
The ROC Curve plots the true positive rate (sensitivity) against the false positive rate (1 - specificity) at various threshold settings. It provides a visual representation of the classifier’s performance across different threshold levels. The Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC-ROC) quantifies the overall performance of the model in distinguishing between the positive and negative classes. A higher AUC-ROC value indicates better discrimination performance.
library(pROC)
library(ggplot2)
# Compute predicted probabilities
predicted_probabilities <- predict(mod_regLogistic_cv, newdata = test_data, type = "prob")
# Extract probabilities for the positive class
positive_probabilities <- predicted_probabilities$"0"
# Compute ROC curve and AUC-ROC
roc_curve <- pROC::roc(test_data$target, positive_probabilities)
auc_roc <- pROC::auc(roc_curve)
# Plot ROC curve with descriptive axis titles
ggroc(roc_curve, color = "steelblue", size = 1) +
labs(title = "Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve",
x = "False Positive Rate (1 - Specificity)",
y = "True Positive Rate (Sensitivity)") +
theme_minimal()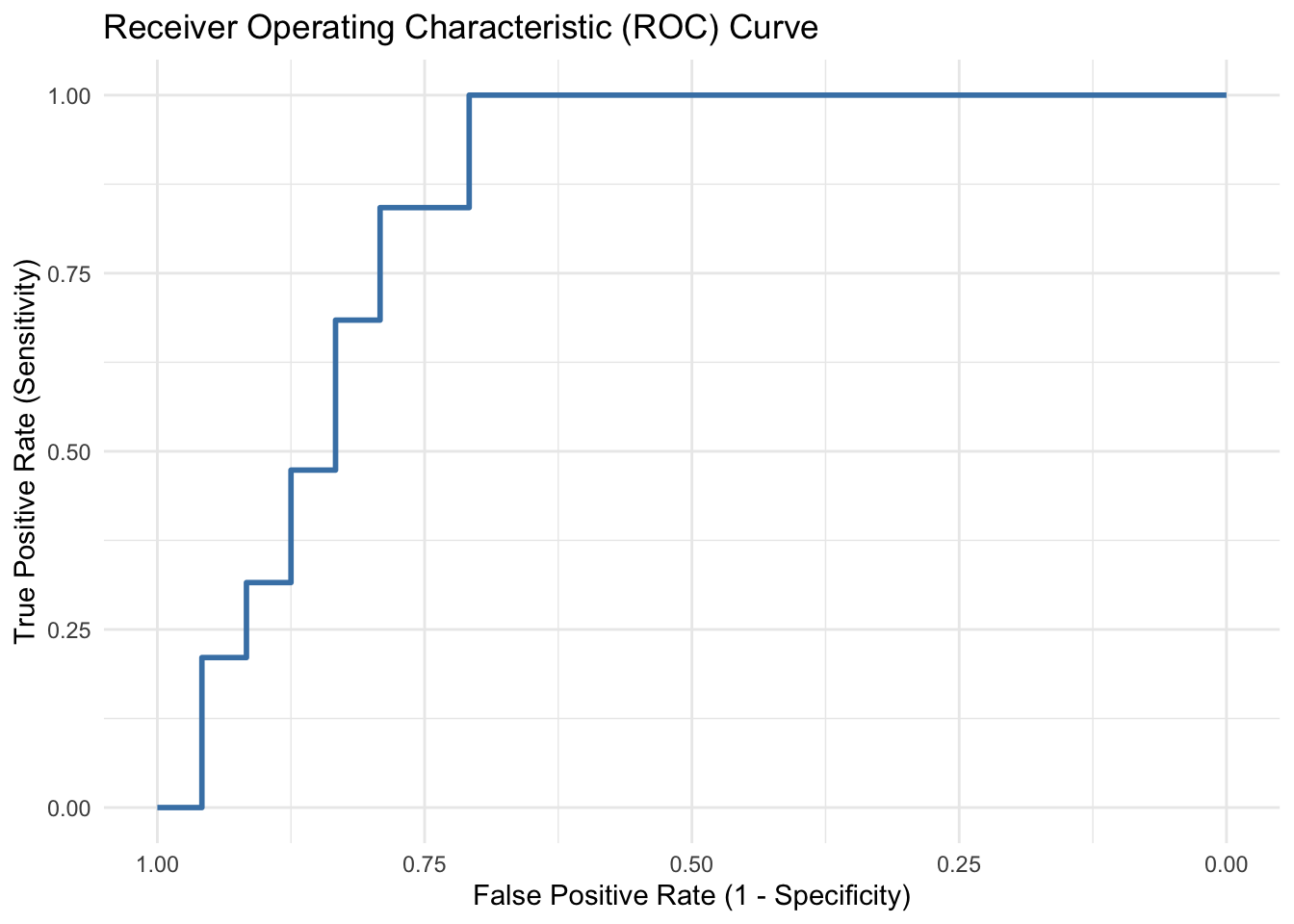
# Print AUC-ROC
cat("AUC-ROC:", auc_roc)
AUC-ROC: 0.8486842